Social-emotional learning is kind of like matcha. You hear about it, you notice it on your social media feed, and for a while, you think it’s just another trend.
But later, you realize that the hype might be real. With the trendy green drink, people slowly determined that matcha holds major benefits such as improving cardio health, reducing cancer risk, lowering blood glucose, and increasing metabolism (to name a few).
Just like matcha, social-emotional learning (SEL) isn’t simply a fad that’ll pass in time.
What is social-emotional learning?
SEL is an educational framework that helps teach important skills and knowledge that are critical for academic (and long-term) success.
Specifically, SEL is related to developing a healthy self-image, regulating emotions, developing goals, nurturing relationships, and making responsible decisions.
During the pandemic’s surges, we were all trying to get used to the unfamiliar remote working environments. This meant tapping into our non-verbal communication skills and learning how to work together when physically apart.
And one result was that educators began recognizing the importance and necessity of SEL in the classroom. More significantly, researchers continue confirming that SEL is critical for reducing pandemic learning losses.
Five Social-Emotional Learning Competencies
There are five main components to SEL:
1. Self-awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to identify and develop your thoughts, feelings, values, and emotions. Having self-awareness enables you to take these—and improve your behavior. When you have self-awareness, you’re more able to identify strengths and weaknesses, and from there, positively influence your actions, decisions, goals, and outcomes.
For example, imagine you grew up constantly receiving criticism. Through your life, maybe you developed a habit of shutting down when faced with any type of criticism (or even just feedback). And perhaps the consequence is that you’re stuck in this cycle, which may lead to conflict in school, work, and your personal life.
By developing self-awareness, you can identify that behavior (shutting down), look at how it’s affecting potential outcomes, and then slowly develop new behaviors.
2. Self-management
Self-management refers to your ability to regulate and control your emotions. By developing self-management, you hone your ability to manage how your emotions may influence certain areas of your life. Self-management can lead to greater stress management, organizational skills, goal setting, impulse-control, and self-discipline.
With self-management, you’ll be more able to understand why you’re feeling some type of way—then, you can develop ways to proactively manage your emotions and ultimately have more positive outcomes.
3. Social awareness
Developing social awareness is related to your ability to relate and empathize with others and their own situations. Ultimately, cultivating social awareness can enable you to develop more positive social relationships and interactions.
For instance, let’s say your friend is telling you about how they’re having a conflict with a family member. If you have social awareness, you’ll be able to recognize whether they’re looking for a) concrete advice or b) just a listener. If you haven’t developed that social awareness, you likely won’t be able to read the room—and that can result in a less gratifying interaction for both parties.
4. Relationship skills
Similarly to the component above, developing relationship skills is related to your ability to navigate social relationships. When you improve your relationship skills, you improve your ability to connect with others—and in turn, your ability to be considerate of others’ emotions in social situations. Consequently, it’ll be easier to develop and maintain positive relationships.
When you improve your relationship skills, you’ll improve areas such as:
- Listening skills
- Verbal & non-verbal communication
- Team-building skills
5. Responsible decision-making
Responsible decision-making is the ability to make constructive decisions based on personal and societal considerations, such as goals, ethical standards, social norms, and safety concerns.
When you develop responsible decision-making skills, you’re more able to consider consequences in any given situation. In addition, this is related to understanding your personal strengths and limitations, as well as considering necessary support when making major decisions.
Why is social-emotional learning important for students?
SEL is valuable to students for a number of reasons. When students develop social-emotional skills, they gain crucial life skills including:
- Identifying emotions
- Cultivating a positive self-image
- Taking responsibility for behavior
- Developing positive relationships
- Building confidence
And as a result, such skills enable students to improve their academic performance, reduce negative social behaviors such as bullying, and develop positive peer and teacher relationships.
Furthermore, these skills are important beyond the K-12 years. SEL guides students to cultivate skills that are crucial in college and the workforce, such as:
- Setting and achieving goals
- Solving problems
- Finding resilience in the face of adversity
- Acting as a leader
In fact, a 2015 survey of employers listed the “ability to work in a team” as the most attractive quality in new college graduates.
In addition, a Forbes report on most desirable skills in college graduates ranked the following at the top of the list:
- Teamwork skills
- Problem-solving skill
- Decision-making skills
- Verbal communication skills
In both higher education and their careers, students will be faced with situations where they must work cooperatively in a group, identify problems and reachable goals, and persevere when faced with difficulty.
Benefits of teaching social-emotional learning in school
Equipping students with tools related to social-emotional learning is key to improving the classroom and each student’s experience.
For instance, when students are better able to understand and identify their emotions, they’re more capable of constructively dealing with any given situation. And when students are in social situations, SEL skills will enable them to cultivate empathy and in turn, respond in a positive manner—and maybe help a struggling friend.
Notably, SEL empowers students to nurture their interpersonal skills, which are often essential later in life—especially if students want to work alongside others. Additionally, SEL guides students to develop emotional intelligence. This is an irreplaceable skill that can serve students in their careers. It enables them to not only manage their own emotions, but identify others’ emotions—and then empathize and provide guidance through tense situations.
Here’s what the research says
Research continues to verify that teaching and learning these skills is incredibly valuable.
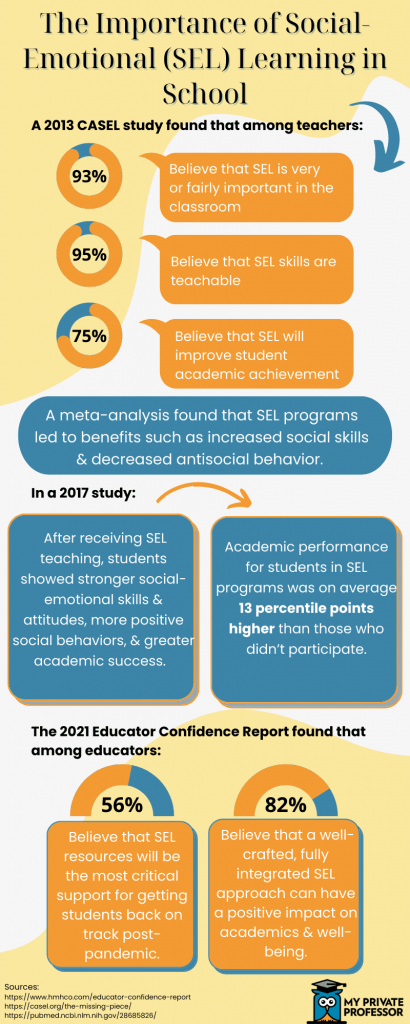
For instance, a meta-analysis on the impact of SEL on students analyzed 213 studies involving more than 270,000 students. The analysis found that:
- Students who participated in SEL programs focusing on the main five competencies increased their academic performance by 11 percentage points compared to students who didn’t participate.
- Students in the SEL programs showed improved classroom behavior, greater ability to manage stress and depression, and more positive attitudes about themselves, others, and school.
Additionally, a recent review on the effectiveness of school-based interventions demonstrated that universal SEL interventions enhance students’ social and emotional skills. In addition, it found that these interventions can reduce depression and anxiety.
SEL also benefits teachers
In order to develop a more positive classroom environment and experience, we’ve got to also consider the other major party involved: teachers.
SEL helps teachers manage stress and burnout—issues which are incredibly prevalent today. According to a RAND survey, teachers were almost three times more at risk for experiencing depression than other adults. And this is due to stress that the job brings.
Just like the benefits SEL brings students, SEL empowers teachers to be more in tune with their emotions and stress/emotional triggers. When they’re able to identify these, they’re better able to manage their feelings constructively. For instance, if they understand what triggers them, they can start being proactive in combatting the cycle.
And when teachers are more emotionally sound, they are more able to provide quality teaching.
SEL can also help teachers make better decisions in stressful situations, and assist them in cultivating healthier student-teacher relationships.
SEL empowers teachers
Importantly, SEL encourages teachers to more frequently practice self-care and prioritize their needs. And when they nurture their health and wellbeing, they experience less anxiety, hyperactivity, and aggression.
Then, consequently, teachers experience negative emotions less frequently—they are happier, and thus more attentive in the classroom. The bottom line is that when teachers show up for themselves, they can more effectively show up for their students.
According to research,
“Emotionally exhausted teachers may use reactive and punitive responses that contribute to negative classroom climates and student-teacher relationships.”
When teachers are happier and healthier, they often rediscover their love for teaching. The ultimate result? A happier and healthier learning environment.
So no, social-emotional learning isn’t just a trendy sideshow—but part of the main act.
Author: Lydia Schapiro